Java編程內(nèi)功-數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)與算法「稀疏數(shù)組」
作者:Java精髓
當(dāng)一個數(shù)組中大部分元素為0,或者為同一個值的數(shù)組時,可以使用稀疏數(shù)組來保存該數(shù)組,本篇就給大家介紹關(guān)于稀疏數(shù)組的相關(guān)知識。
基本介紹
當(dāng)一個數(shù)組中大部分元素為0,或者為同一個值的數(shù)組時,可以使用稀疏數(shù)組來保存該數(shù)組.
稀疏數(shù)組的處理方法是:
- 記錄數(shù)組一共有幾行幾列,有多少個不同的值.
- 把具有不同值的元素的行列記錄在一個小規(guī)模的數(shù)組中,從而縮小程序的規(guī)模.
舉例說明
原始的二維數(shù)組
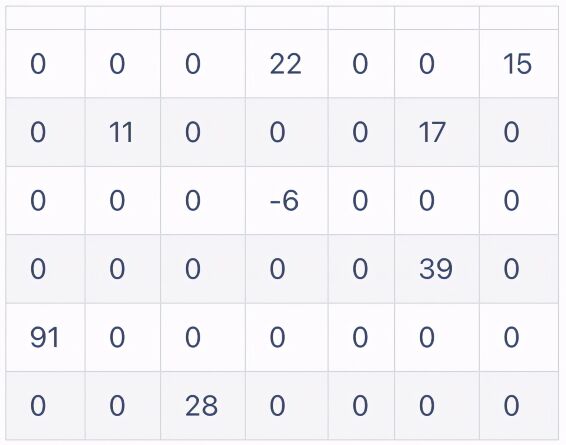
原始的二維數(shù)組
轉(zhuǎn)換后的二維數(shù)組
第一行記錄原始數(shù)組有多少行列,多少值(8<<代表原始數(shù)組的值的個數(shù)22,15,11,17,-6,39,91,28>>)
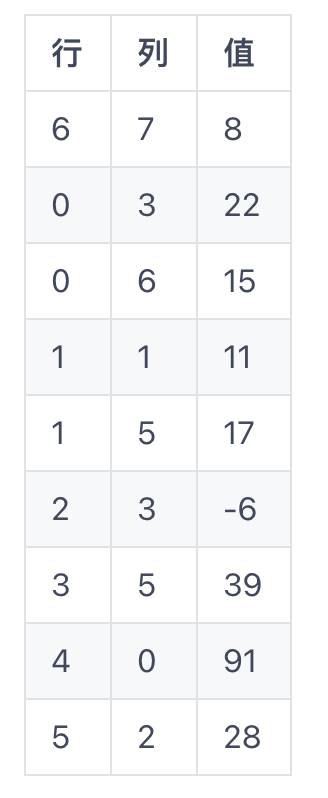
轉(zhuǎn)換后的二維數(shù)組
二維數(shù)組轉(zhuǎn)稀疏數(shù)組思路
- 遍歷原始的二維數(shù)組,得到有效數(shù)據(jù)的個數(shù)sum
- 根據(jù)sum就可以創(chuàng)建稀疏數(shù)組sparseArr int(sum+1)(3)
- 將二維數(shù)組的有效數(shù)據(jù)存入到稀疏數(shù)組
稀疏數(shù)組轉(zhuǎn)原始二維數(shù)組思路
- 先讀取稀疏數(shù)組的第一行,根據(jù)第一行的數(shù)據(jù),創(chuàng)建原始的二維數(shù)組
- 再讀取稀疏數(shù)組后幾行的數(shù)據(jù),并賦給原始的二維數(shù)組即可.
應(yīng)用實(shí)例
- 使用稀疏數(shù)組,來保留類似前面的二維數(shù)組(棋盤\地圖)等
- 把稀疏數(shù)組存盤,并且可重新恢復(fù)原來的二維數(shù)組數(shù)
代碼案例
- package com.structures.sparsearray;
- public class SparseArray {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //創(chuàng)建一個原始的二維數(shù)組11*11
- //0:表示沒有棋子,1表示黑子,2表示白子
- int[][] chessArr1 = new int[11][11];
- chessArr1[1][2] = 1;
- chessArr1[2][3] = 2;
- //輸出原始二維數(shù)組
- System.out.println("原始的二維數(shù)組");
- for (int[] ints : chessArr1) {
- for (int anInt : ints) {
- System.out.printf("%d\t", anInt);
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- //將二維數(shù)組轉(zhuǎn)稀疏數(shù)組
- //1.先遍歷二維數(shù)組,得到非0數(shù)據(jù)的個數(shù).
- int sum = 0;
- for (int[] ints : chessArr1) {
- for (int anInt : ints) {
- if (anInt != 0) {
- sum++;
- }
- }
- }
- System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
- //2.創(chuàng)建對應(yīng)的稀疏數(shù)組
- int[][] sparseArr = new int[sum + 1][3];
- //給稀疏數(shù)組賦值
- sparseArr[0][0] = 11;
- sparseArr[0][1] = 11;
- sparseArr[0][2] = sum;
- //遍歷原始數(shù)組,將非0的值存放到稀疏數(shù)組中
- int count = 0;//count用于記錄第幾個非0數(shù)據(jù)
- for (int i = 0; i < chessArr1.length; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < chessArr1[i].length; j++) {
- if (chessArr1[i][j] != 0) {
- count++;
- sparseArr[count][0] = i;
- sparseArr[count][1] = j;
- sparseArr[count][2] = chessArr1[i][j];
- }
- }
- }
- //輸出稀疏數(shù)組
- System.out.println();
- System.out.println("得到的稀疏數(shù)組為~~~~");
- for (int[] ints : sparseArr) {
- for (int anInt : ints) {
- if (anInt != 0) {
- System.out.printf("%d\t", anInt);
- }
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- //將稀疏數(shù)組恢復(fù)成原始數(shù)組
- int[][] chessArr2 = new int[sparseArr[0][0]][sparseArr[0][1]];
- for (int i = 0; i < sparseArr[0][2]; i++) {
- chessArr2[sparseArr[i + 1][0]][sparseArr[i + 1][1]] = sparseArr[i + 1][2];
- }
- //恢復(fù)后的原始數(shù)組
- System.out.println("恢復(fù)后的原始數(shù)組");
- for (int[] ints : chessArr2) {
- for (int anInt : ints) {
- System.out.printf("%d\t", anInt);
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
- }
- /*
- 原始的二維數(shù)組
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- sum = 2
- 得到的稀疏數(shù)組為~~~~
- 11 11 2
- 1 2 1
- 2 3 2
- 恢復(fù)后的原始數(shù)組
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
- */
【編輯推薦】
責(zé)任編輯:姜華
來源:
今日頭條



























